ELEKTRIK VE MANYETİZMA DERSİ BİLGİ FORMU
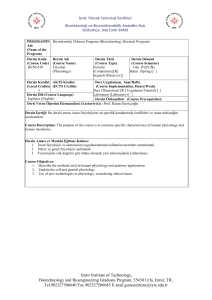
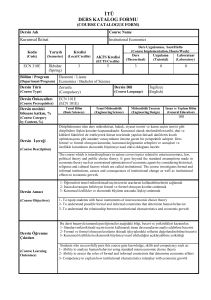
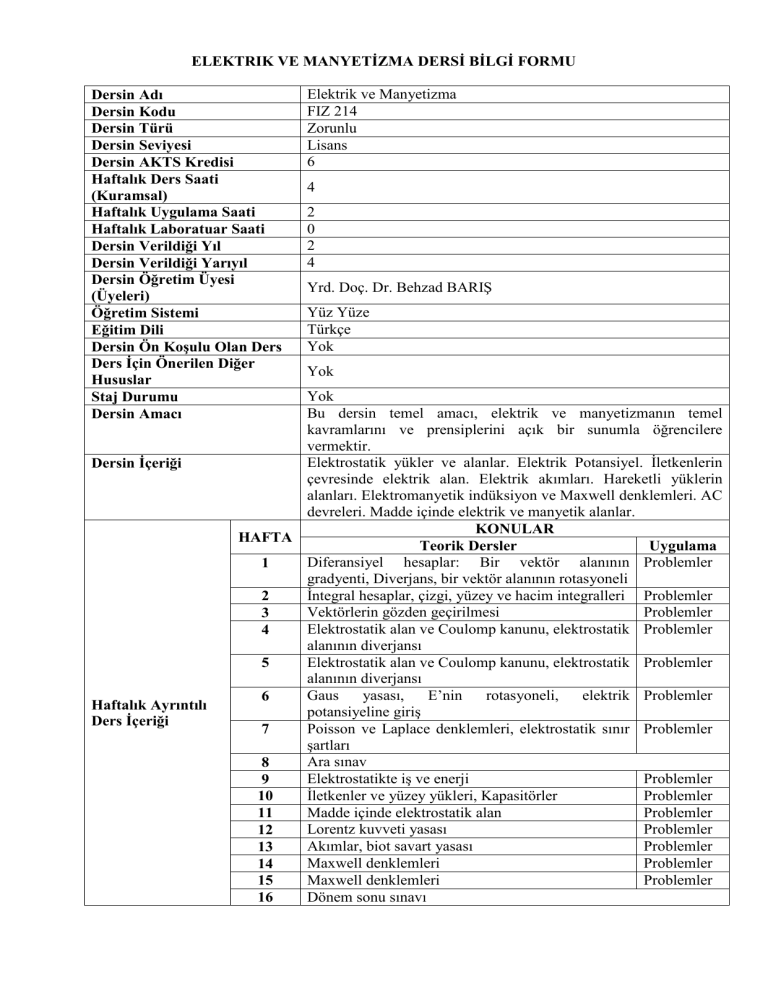
Dersin Adı
Dersin Kodu
Dersin Türü
Dersin Seviyesi
Dersin AKTS Kredisi
Haftalık Ders Saati
(Kuramsal)
Haftalık Uygulama Saati
Haftalık Laboratuar Saati
Dersin Verildiği Yıl
Dersin Verildiği Yarıyıl
Dersin Öğretim Üyesi
(Üyeleri)
Öğretim Sistemi
Eğitim Dili
Dersin Ön Koşulu Olan Ders
Ders İçin Önerilen Diğer
Hususlar
Staj Durumu
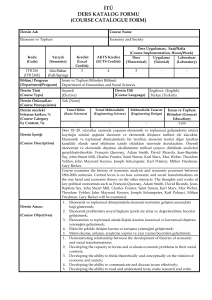
Dersin Amacı
Dersin İçeriği
Haftalık Ayrıntılı
Ders İçeriği
Elektrik ve Manyetizma
FIZ 214
Zorunlu
Lisans
6
4
2
0
2
4
Yrd. Doç. Dr. Behzad BARIŞ
Yüz Yüze
Türkçe
Yok
Yok
Yok
Bu dersin temel amacı, elektrik ve manyetizmanın temel
kavramlarını ve prensiplerini açık bir sunumla öğrencilere
vermektir.
Elektrostatik yükler ve alanlar. Elektrik Potansiyel. İletkenlerin
çevresinde elektrik alan. Elektrik akımları. Hareketli yüklerin
alanları. Elektromanyetik indüksiyon ve Maxwell denklemleri. AC
devreleri. Madde içinde elektrik ve manyetik alanlar.
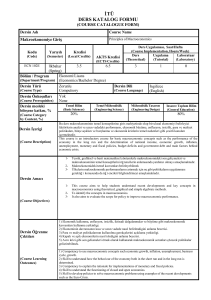
KONULAR
HAFTA
Teorik Dersler
Uygulama
Diferansiyel hesaplar: Bir vektör alanının Problemler
1
gradyenti, Diverjans, bir vektör alanının rotasyoneli
İntegral hesaplar, çizgi, yüzey ve hacim integralleri Problemler
2
Vektörlerin gözden geçirilmesi
Problemler
3
Elektrostatik alan ve Coulomp kanunu, elektrostatik Problemler
4
alanının diverjansı
Elektrostatik alan ve Coulomp kanunu, elektrostatik Problemler
5
alanının diverjansı
Gaus
yasası,
E’nin
rotasyoneli,
elektrik Problemler
6
potansiyeline giriş
Poisson ve Laplace denklemleri, elektrostatik sınır Problemler
7
şartları
Ara sınav
8
Elektrostatikte iş ve enerji
Problemler
9
İletkenler ve yüzey yükleri, Kapasitörler
Problemler
10
Madde içinde elektrostatik alan
Problemler
11
Lorentz kuvveti yasası
Problemler
12
Akımlar, biot savart yasası
Problemler
13
Maxwell denklemleri
Problemler
14
Maxwell denklemleri
Problemler
15
Dönem
sonu
sınavı
16
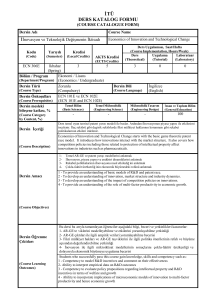
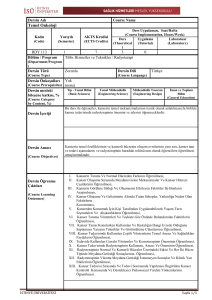
Öğrenme Çıktıları
ÖÇ - 1: Elektrik ve manyetizmadaki bağıntı ve kuralları formüle edebilecek
ve problemleri çözebilecek.
ÖÇ - 2: Coulomb ve Gauss yasalarını kullanarak elektrostatikte problemleri
çözebilecek ve basit yük dağılımlarını içeren durumları hayal
edebilecek.
ÖÇ– 3:Biot-Savart ve Amper yasalarını kullanarak basit bir akım
dağılımından meydana gelen manyetik alanı tanımlayabilecek ve
Lorentz yasasını kullanarak manyetik alan ile hareket eden yük (veya
akım) arasındaki etkileşimi içeren problemleri çözebilecek.
ÖÇ - 4: Manyetik alanın değişmesi veya hareket eden bir halkadan meydana
gelen indüklenen EMK'yı tanımlayabilecek.
ÖÇ - 5: Farklı tiplerdeki manyetik malzemelerin karakteristik özelliklerini
tanımlayabilecek ve manyetik çevrim problemlerini çözebilecek.
Ders Kitabı/
Malzemesi/
Önerilen
Kaynaklar
DERS KİTABI:
1- E. M. Purcell, McGraw-Hill, 1985;Electricity and Magnetism, Berkeley
Physics Course, Volume2, 2nd Edition
2- Vector Analysis, Spiegel, Schaum Outline Series
3- Mary L. Boas, John Wiley, NY, !966; Mathematical Methods in the
Physical Science
4- Griffiths, Electromagnetic Theory
DERS ARAÇLARI:
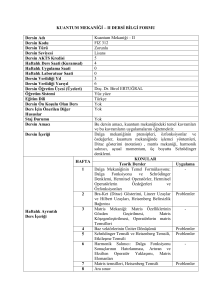
DEĞERLENDİRME
Yarıyıl (Yıl) İçi
Sayısı
Yarıyıl (Yıl) Notuna Katkısı %
Etkinlikleri
Ara sınav
1
100
100
TOPLAM
1
40
Yarıyıl (Yıl) İçi Etkinliklerinin Başarı
Notuna Katkısı
60
Yarıyıl (Yıl) Sonu Sınavının Başarı
Notuna Katkısı
100
TOPLAM
Dersin Öğrenme, Öğretme ve Değerlendirme Etkinlikleri Çerçevesinde
İş Yükünün Hesaplanması
Süresi
Toplam İş Yükü
Etkinlikler
Sayısı
(Saat)
(Saat)
Haftalık ders saati (Kuramsal)
14
4
56
Haftalık ders saati (Uygulama)
14
2
28
Sınıf dışı çalışma
14
4
56
Ara sınav için hazırlık
1
16
16
Ara sınav
1
2
2
Dönem sonu sınavı için hazırlık
1
20
20
Dönem sonu sınavı
1
2
2
TOPLAM İŞ YÜKÜ (Saat) = 180
DERSİN AKTS KREDİSİ= Toplam İş Yükü(saat)/(30saat/AKTS)= 6
Program ve Öğrenme Çıktıları İlişkisi
Program Çıktıları
Ders
Öğrenme
Çıktıları PÇ PÇ PÇ PÇ PÇ PÇ PÇ PÇ PÇ PÇ PÇ PÇ
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9 10 11 12
ÖÇ 1
ÖÇ 2
ÖÇ 3
ÖÇ 4
ÖÇ 5
ÖÇ 6
ÖÇ 7
ÖÇ 8
ÖÇ 9
ÖÇ 10
ÖÇ 11
ÖÇ 12
*Katkı Düzeyi: 1 Çok düşük
2 Düşük
3 Orta
4 Yüksek
5 Çok yüksek
ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM INDIVIDUAL COURSE DESCRIPTION
Course Unit Title
Course Unit Code
Type of Course Unit
Level of Course Unit
Number of ECTS Credits Allocated
Theoretical (hour/week)
Practice (hour/week)
Laboratory (hour/week)
Year of Study
Semester when the course unit is
delivered
Name of Lecturer (s)
Mode of Delivery
Language of Instruction
Prerequisities and co-requisities
Recommended Optional
Programme Components
Work Placement(s)
Objectives of the Course
Course Contents
WEEKS
1
2
3
4
5
Weekly Detailed
Course Contents
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
Electricity and Magnetism
FIZ 214
Compulsory
Undergraduate
6
4
2
0
2
4
Assistant Prof. Dr. Behzad BARIŞ
Face to Face
Turkish
None
None
None
The main objectives of this course are to provide the student
with a clear presentation of the main concepts and principles of
electricity and magnetism.
Electrostatic charges and fields. Electrical Potential. Electric
field around conductors. Electric currents. Fields of moving
charges. Electromagnetic induction and Maxwell equations.
AC circuits. Electric and magnetic fields in matter.
TOPICS
Theoretical Courses
Application
Differential Calculus: Gradient of a vector field.
Problems
Divergence. Curl of a vector field.
Integral Calculus: Line, surface and volume
Problems
integrals
Vector Review
Problems
The Electrostatic Field and Coulomb's
Problems
Law.Divergence of Electrostatic Fields
The Electrostatic Field and Coulomb's
Problems
Law.Divergence of Electrostatic Fields
Gauss Law. The Curl of E. Introduction to the
Problems
Electrical Potential
Poissons's and Laplace's Equation. Electrostatic
Problems
Boundary Conditions
Mid-term exam
Work and Energy in Electrostatic
Problems
Conductors and Surface Charge. Capacitors
Problems
Electrostatic Fields in Matter
Problems
The Lorentz Force Law
Problems
Currents, The Biot Savart Law
Problems
Maxwell Equations
Problems
Maxwell Equations
Problems
End-of-term exam
Learning Outcomes
Textbook/ Material/
Recommended
Readings
LO - 1: Formulate laws and relationships in Electricity and Magnetism, and
to solve problems.
LO - 2: Solve problems in electrostatics using Coulomb’s Law, Gauss' Law,
and Image Method for cases involving simple charge distributions.
LO - 3:Determine the magnetic field due to simple current distributions
using Biot-Savart Law and Ampere's Circuital Law, and solve
problems involving the interaction between moving charge (or
current) and magnetic field using Lorentz Law.
LO - 4: Determine the induced emk arising from changing magnetic field
and moving circuits.
LO - 5: Describe the characteristics of different types of magnetic materials
and solve problems in magnetic circuits.
Course Book:
1- E. M. Purcell, McGraw-Hill, 1985;Electricity and Magnetism, Berkeley
Physics Course, Volume2, 2nd Edition
2- Vector Analysis, Spiegel, Schaum Outline Series
3- Mary L. Boas, John Wiley, NY, !966; Mathematical Methods in the
Physical Science
4- Griffiths, Electromagnetic Theory
Course Materials:
ASSESSMENT
Semester (Year) Interior
Number
Activities
Laboratory test reports
Laboratory practical exam
Homework
Supervision
1
TOTAL
1
Semester (year) Grades of Domestic
Contribution Activities
Semester (year) of the Final Exam grade
Contribution
TOTAL
Semester (year) Note the %
Contribution to
100
100
40
60
100
Course Learning, Teaching and Assessment Activities in the
Framework Calculation of the workload
Duration
Total workload
Activities
Number
(hour)
(hour)
Hours per week (Theoretical)
14
4
56
Hours per week (Application)
14
2
28
Own (personal) studies outside class
14
4
56
Own study for first mid-term exam
1
16
16
Mid-term exam
1
2
2
Own study for end-of-term exam
1
20
20
End-of-term exam
1
2
2
TOTAL WORKLOAD (hour) = 180
AKTS CREDIT COURSE= Total Work Load(hour)/(30 hours/AKTS)= 6
Contribution of Learning Outcomes to Programme Outcomes
Programme Outcomes
Learning
Outcomes
PO
1
PO
2
PO
3
PO
4
PO
5
PO
6
PO
7
PO
8
PO
9
PO
10
PO
11
PO
12
LO 1
LO 2
LO 3
LO 4
LO 5
LO 6
LO 7
LO 8
LO 9
LO 10
LO 11
LO 12
*Contribution Level: 1 Very Low
2 Low
3 Medium
4 High
5 Very High